Securing database with command line linux: Difference between revisions
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
'''What root mean ?''' | '''What root mean ?''' | ||
[[File:Pagename explanation rootuserjpg|thumb|Root user in command line]] | |||
*root is the user name or account that by default has access to all commands and files on a Linux or other Unix-like operating system. It is also referred to as the root account, root user and the superuser. | *root is the user name or account that by default has access to all commands and files on a Linux or other Unix-like operating system. It is also referred to as the root account, root user and the superuser. | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 21 April 2016
Aim of this page
- To know information about Linux operation system.
- To secure the database using the command line method.
- What is sudo (superuser) ?
- What is the root user ?
- Control the command line environment.
- Access the information in database by easy way.
Information about Linux operation system and Database
- What is Linux?
Linux is, in simplest terms, an operating system. It is the software on a computer that enables applications and the computer operator to access the devices on the computer to perform desired functions. The operating system (OS) relays instructions from an application to, for instance, the computer's processor. The processor performs the instructed task, then sends the results back to the application via the operating system. Explained in these terms, Linux is very similar to other operating systems, such as Windows and OS X. But something sets Linux apart from these operating systems. The Linux operating system represented a $25 billion ecosystem in 2008. Since its inception in 1991, Linux has grown to become a force in computing, powering everything from the New York Stock Exchange to mobile phones to supercomputers to consumer devices.
As an open operating system, Linux is developed collaboratively, meaning no one company is solely responsible for its development or ongoing support. Companies participating in the Linux economy share research and development costs with their partners and competitors. This spreading of development
burden amongst individuals and companies has resulted in a large and efficient ecosystem and unheralded software innovation. Over 1,000 developers, from at least 100 different companies, contribute to every kernel release. In the past two years alone, over 3,200 developers from 200 companies have contributed to the kernel--which is just one small piece of a Linux distribution.
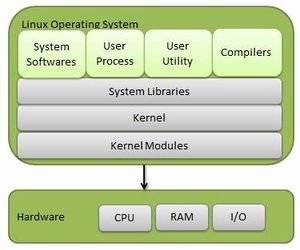
- Components of Linux System
Linux Operating System has primarily three components
1) Kernel - Kernel is the core part of Linux. It is responsible for all major activities of this operating system. It is consists of various modules and it interacts directly with the underlying hardware. Kernel provides the required abstraction to hide low level hardware details to system or application programs.
2) System Library - System libraries are special functions or programs using which application programs or system utilities accesses Kernel's features. These libraries implements most of the functionalities of the operating system and do not requires kernel module's code access rights.
3) System Utility - System Utility programs are responsible to do specialized, individual level tasks.
- Kernel Mode VS User Mode
Kernel component code executes in a special privileged mode called kernel mode with full access to all resources of the computer. This code represents a single process, executes in single address space and do not require any context switch and hence is very efficient and fast. Kernel runs each processes and provides system services to processes, provides protected access to hardwares to processes.
Support code which is not required to run in kernel mode is in System Library. User programs and other system programs works in User Mode which has no access to system hardwares and kernel code. User programs/ utilities use System libraries to access Kernel functions to get system's low level tasks.
Basic Features
Following are some of the important features of Linux Operating System.
- Portable - Portability means softwares can works on different types of hardwares in same way.Linux kernel and application programs supports their installation on any kind of hardware platform.
- Open Source - Linux source code is freely available and it is community based development project. Multiple teams works in collaboration to enhance the capability of Linux operating system and it is continuously evolving.
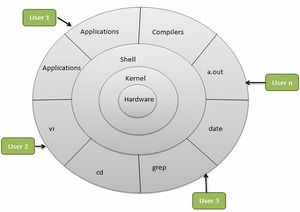
- Multi-User - Linux is a multiuser system means multiple users can access system resources like memory/ ram/ application programs at same time.
- Multiprogramming - Linux is a multiprogramming system means multiple applications can run at same time.
- Hierarchical File System - Linux provides a standard file structure in which system files/ user files are arranged.
- Shell - Linux provides a special interpreter program which can be used to execute commands of the operating system. It can be used to do various types of operations, call application programs etc.
- Security - Linux provides user security using authentication features like password protection/ controlled access to specific files/ encryption of data.
Linux System Architecture is consists of following layers
- Hardware layer - Hardware consists of all peripheral devices (RAM/ HDD/ CPU etc).
- Kernel - Core component of Operating System, interacts directly with hardware, provides low level services to upper layer components.
- Shell - An interface to kernel, hiding complexity of kernel's functions from users. Takes commands from user and executes kernel's functions.
- Utilities - Utility programs giving user most of the functionalities of an operating systems.
What database mean ?
A database is an organized collection of data. It is the collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views and other objects. The data are typically organized to model aspects of reality in a way that supports processes requiring information, such as modelling the availability of rooms in hotels in a way that supports finding a hotel with vacancies.
What sudo mean in Linux ?
Sudo (superuser do) allows a system administrator to give certain users (or groups of users) the ability to run some (or all) commands as root while logging all commands and arguments. Sudo operates on a per-command basis. It is not a replacement for the shell. Features include: the ability to restrict what commands a user may run on aper-host basis, copious logging of each command (providing a clear audit trail of who did what), a configurable timeout of the sudo command, and the ability to use the same configuration file (sudoers) on many different machines.
What root mean ?
- root is the user name or account that by default has access to all commands and files on a Linux or other Unix-like operating system. It is also referred to as the root account, root user and the superuser.
- The word root also has several additional, related meanings when used as part of other terms, and thus it can be a source of confusion to people new to Unix-like systems.
- One of these is the root directory, which is the top level directory on a system. That is, it is the directory in which all other directories, including their subdirectories, and files reside. The root directory is designated by a forward slash ( / ).
- Another is /root (pronounced slash root), which is the root user's home directory. A home directory is the primary repository of a user's files, including that user's configuration files, and it is usually the directory in which a user finds itself when it logs into a system. /root is a subdirectory of the root directory, as indicated by the forward slash that begins its name, and should not to be confused with that directory. Home directories for users other than root are by default created in the /home directory, which is another standard subdirectory of the root directory.
- Root privileges are the powers that the root account has on the system. The root account is the most privileged on the system and has absolute power over it (i.e., complete access to all files and commands). Among root's powers are the ability to modify the system in any way desired and to grant and revoke access permissions (i.e., the ability to read, modify and execute specific files and directories) for other users, including any of those that are by default reserved for root.
General Information about command line
- Starting using the command line Linux
- Before starting you need to take a short course of command line in code academy Code Academy
- After you finish the command line exercises for the command line you need to know a few commands that you have to remember always
- First [cd] the command that will make you navigate everywhere in the command line environment
- The simple commands that will make you feel free in Linux environment if you are using Windows or Mac
- second [pwd] command that always you will know your location in the system
References
[1] Linux information [2]Operating System - Linux [3] Sudo definition [4] Root meaning in Linux operation system