Logging&monitoring: Difference between revisions
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
The Aim of this wiki page is to give an introduction to Logging and Monitoring application called Graylog, what are the main benefits of it and how to install it on Ubuntu Machine. | The Aim of this wiki page is to give an introduction to Logging and Monitoring application called Graylog, what are the main benefits of it and how to install it on Ubuntu Machine. | ||
*''' | *'''Logging and monitoring''' | ||
Logging is the process of keeping a continuous record of an event. | |||
The general rule of logging is: Log everything which is not predictable. | |||
Monitoring is the process of observing and checking the progress or quality of something over a period of time; keep under systematic review.<ref>[https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/monitor]</ref> | |||
Monitoring cannot be achieved without logging. That is the reason integrated solutions combine the two processes. | |||
Monitoring is used to: | |||
*check performance | |||
*detect if something worth noticing happened | |||
*prevent something to happen | |||
*detect whether a system is under attack | |||
*'''The best solution for logging''' | *'''The best solution for logging''' | ||
As of today, [https://www.graylog.org Graylog] is the most popular open-source solution for logging and monitoring computer systems before [https://www.elastic.co/webinars/introduction-elk-stack ELK stack]. | |||
In the proprietary world, [https://www.splunk.com Splunk] is the leader. | |||
This article describes Graylog solution. | |||
Graylog is made of three components: | |||
*Elasticsearch as the documents indexing engine | |||
*Mongodb for database | |||
*Graylog itself (server and web interface combined) to collect and view logs | |||
The main advantages of Graylog are: | |||
*Open-source | |||
*Works with unstructured logs and from any source | |||
*Good looking interface and dashboards | |||
*Supports user management (LDAP) | |||
*'''Why we should logging our servers''' | *'''Why we should logging our servers''' | ||
*'''Securing during logging''' | *'''Securing during logging''' | ||
Revision as of 23:42, 5 October 2016
Logging and Monitoring - Logging Solution - Graylog
Team: Artur Ovtsinnikov, Mohanad Aly, Etienne Barrier, Meelis Hass
Group : Cyber Security Engineering (C21)
Page Created: 18 September 2016
Last modified: 05 October 2016
Aim of this page
The Aim of this wiki page is to give an introduction to Logging and Monitoring application called Graylog, what are the main benefits of it and how to install it on Ubuntu Machine.
- Logging and monitoring
Logging is the process of keeping a continuous record of an event. The general rule of logging is: Log everything which is not predictable.
Monitoring is the process of observing and checking the progress or quality of something over a period of time; keep under systematic review.[1] Monitoring cannot be achieved without logging. That is the reason integrated solutions combine the two processes. Monitoring is used to:
- check performance
- detect if something worth noticing happened
- prevent something to happen
- detect whether a system is under attack
- The best solution for logging
As of today, Graylog is the most popular open-source solution for logging and monitoring computer systems before ELK stack. In the proprietary world, Splunk is the leader.
This article describes Graylog solution. Graylog is made of three components:
- Elasticsearch as the documents indexing engine
- Mongodb for database
- Graylog itself (server and web interface combined) to collect and view logs
The main advantages of Graylog are:
- Open-source
- Works with unstructured logs and from any source
- Good looking interface and dashboards
- Supports user management (LDAP)
- Why we should logging our servers
- Securing during logging
Topology of the Elab system
Desktop machine
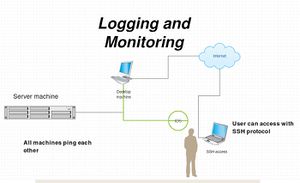
Begin with the basic setup, network configuration and make the machine has internet access which the ip address of the machine is 192.168.56.100
Server machine ip address 192.168.56.200
- Can be connected over ssh with student@192.168.56.200
- Also can connect with other IP address ssh student@10.10.10.10
IDS ip address 192.168.56.201
Starting to update and upgrade the OS
Check for current version
If your machine is running older version then 16.04 which is the latest long term supported version, please follow the following commands to upgrade your machine to the latest version.
- First check your current Ubuntu version by running the following command:
lsb_release -a
If you find that your machine is already running the following version or higher than:
Description:Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS Release:16.04
Then there is no need to upgrade the OS
Upgrade
- First become super user "root":
sudo -i
- Begin by updating the package list:
apt-get update
- Upgrade installed packages to their latest available versions:
apt-get upgrade
- Once upgrade finishes, use the dist-upgrade command, which will perform upgrades involving changing dependencies
apt-get dist-upgrade
- Now that you have an up-to-date installation of Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, you can use
do-release-upgradeto upgrade to the Ubuntu 16.04 LTS release.
Initial Setup for graylog
Prerequisites
Ubuntu Linux machine, sudo access and some Linux beginner skills are needed. The installation of Graylog is not that hard as described on some webpages. In this tutorial the Ubuntu 16.04 64-bit VPS server will be used since it is the latest LTS. Unfortunately, Graylog cannot be installed simply by using one command apt-get install graylog, because there is some prerequisite applications needed for it to work. In this tutorial i will describe the commands, what is needed and how to configure the services to work together with the Graylog, installation is simple! Attention! All links and packages/versions are present to the time of writing this guide it might need to be updated later on.
Step by Step Installation tutorial on Ubuntu 16.04 Linux host machine
1) It is important to have the latest package lists to update them to get info on the newst versions of packages and their dependencies. So we need to run the following command to update them:
Command: sudo apt-get update
2) Now we can install the setup base packages:
Command: apt-get install apt-transport-https openjdk-8-jre-headless uuid-runtime pwgen
3) MongoDB is a Free and open-source cross-platform document-oriented database program written in C++,C and JavaScript. Classified as a NoSQL database program in favor of JSON-like documents with dynamic schemas (format BSON) making the integration of data in certain types of applications like Graylog easier and faster.
The version included in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS can be used together with Graylog 2 and higher, but it is also possible to check the official webpage and download the needed/latest version.
It can be installed by running the following command:
Command: apt-get install mongodb-server
4) Elasticsearch is a search engine based on Lucene written in Java. It provides a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine with an HTTP web interface and schema-free JSON documents.
Elasticsearch is required for Graylog 2 and higher to work, so it is possible to see the complete installation instructions on the official page
Commands:
wget -qO - https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
echo "deb https://packages.elastic.co/elasticsearch/2.x/debian stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elasticsearch-2.x.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install elasticsearch
5) Modifying the Elasticsearch configuration file and setting the cluster name to graylog so it will be visible and accessible by graylog.
Command: nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
and change cluster.name:elasticsearch to cluster.name: graylog
6) After config was modified, we can now start Elasticsearch:
sudo /bin/systemctl daemon-reload
sudo /bin/systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
sudo /bin/systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
It is possible to check if the elasticsearch configured correctly by using the following command:
curl -XGET http://localhost:9200
7) Graylog can now be installed if all the above steps were done successfully First it is needed to install the Graylog repository using the following commands:
wget https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-2.1-repository_latest.deb
sudo dpkg -i graylog-2.1-repository_latest.deb
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install graylog-server
8) After the Graylog has been installed it is needed to change the configuration
Think about the password (which would be used to login) and then use the command:
echo -n supersecretpassword123 | sha256sum
It will generate the sha256 hash of the password which would be needed to copy-pasted and add it to the password_secret and root_password_sha2 in the graylog config (/etc/graylog/server/server.conf). This is mandatory to do! Without it Graylog will not start!
9) In order to connect to Graylog web-interface it is needed to set rest_listen_uri and web_listen_uri to the public hostname or IP address of the machine.
10) Last step is to enable Graylog during the system startup:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable graylog-server.service
sudo systemctl start graylog-server.service
Summary
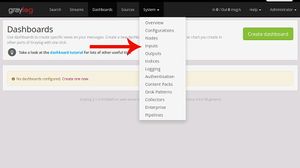
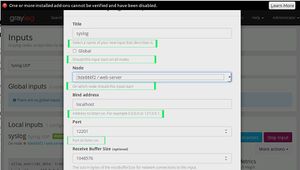
- After setting the graylog and the web interface is working follow the few steps to logging the system
See also
References
2- http://docs.graylog.org/en/2.1/