Logging - Monitoring C21
Logging and Monitoring with Graylog
Course: Logging and Monitoring - Lecturer: Margus Ernits
Group: Cyber Security Engineering (C21)
Team members: Ender Phan, Kustas Kurval, Sheela Gowry Sumathi Raju, Artur Vincent Kerge
Page created on: October 05, 2016
Abstract
In order to understand how to set up the Graylog service as well as understand its crucial roles. We decided to choose Graylog as our application for logging and monitoring. Below are our objectives which would be expected to achieve later on:
- How to install Graylog on Ubuntu 14.04.
- How to use Graylog to protect servers.
- Upgrading and configuring Graylog at first, and know how to secure Graylog.
- Threats and security during logging.
Installation Guide
Ubuntu 14.04
Prerequisites
Since the Elasticsearch is based on java, we would require to install either openJDK or Oracle JDK. It is recommended to install Oracle JDK, verify the java version by using the following command.
Remove the OpenJDK from the system, if you have it already installed. From now on it is presumed that user has root privileges.
apt-get remove --purge openjdk*
Add repository.
add-apt-repository -y ppa:webupd8team/java
Run the following command to pull the packages information from the newly added repository.
apt-get update
Issue the following command to install Java jdk 1.8.
apt-get -y install oracle-java8-installer
java -version
Output:
Java version "1.8.0_60" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_60-b27) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.60-b23, mixed mode)
Installing extras
Elasticsearch
Let’s install Elasticsearch, it can be downloaded from the official website.
Download and install GPG signing key.
wget -qO - https://packages.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
Note that the -qO argument is lowercase Quebec followed by capital Oscar.
Save the repository definition to /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elasticsearch.list
echo "deb http://packages.elastic.co/elasticsearch/2.x/debian stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elasticsearch.list
Update repository cache and install Elasticsearch
apt-get update && apt-get install elasticsearch
Configure Elasticsearch to start during system startup.
update-rc.d elasticsearch defaults
The only important thing is to set a cluster name as “graylog2“, that is being used by graylog. Now edit the configuration file of Elasticsearch.
nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: graylog2
In the same file disable dynamic scripts to avoid remote execution. That can be done by adding the following line:
FOLLOWING LINE GOES INTO GRAYLOG CONF!
script.disable_dynamic: true
Once it is done, we are good to go. Before that, restart the Elasticsearch services to load the modified configuration.
service elasticsearch restart
Wait at least a minute to let the Elasticsearch get fully restarted, otherwise testing will fail. Elastisearch should be now listen on 9200 for processing HTTP request, we can use CURL to get the response. Ensure that it returns with cluster name as “graylog2”
curl -X GET http://localhost:9200
{
"status" : 200,
"name" : "Pistol",
"cluster_name" : "graylog2",
"version" : {
"number" : "1.7.1",
"build_hash" : "b88f43fc40b0bcd7f173a1f9ee2e97816de80b19",
"build_timestamp" : "2015-07-29T09:54:16Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "4.10.4"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Optional: Use the following command to check the Elasticsearch cluster health, you must get a cluster status as “green” for graylog to work.
curl -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty=true'
{
"cluster_name" : "graylog2",
"status" : "green",
"timed_out" : false,
"number_of_nodes" : 1,
"number_of_data_nodes" : 1,
"active_primary_shards" : 0,
"active_shards" : 0,
"relocating_shards" : 0,
"initializing_shards" : 0,
"unassigned_shards" : 0,
"delayed_unassigned_shards" : 0,
"number_of_pending_tasks" : 0,
"number_of_in_flight_fetch" : 0
}
MongoDB
MongoDB is available in deb format and same can be downloaded from the official website. Add the following repository information on the system to install MongoDB. Before that we must import public key.
apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 7F0CEB10
Add repository by creating the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.0.list list file using the command.
echo "deb http://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu trusty/mongodb-org/3.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-3.0.list
Update repository cache.
apt-get update
Install MongoDB using the following command.
apt-get install mongodb-org
Start the MongoDB service and enable it to start automatically during the system start-up.
service mongod start
No /etc/init.d/mongod :( also, why is -s argument needed for ls?
ls -s /usr/bin/mongod /etc/init.d/mongod
update-rc.d mongod defaults
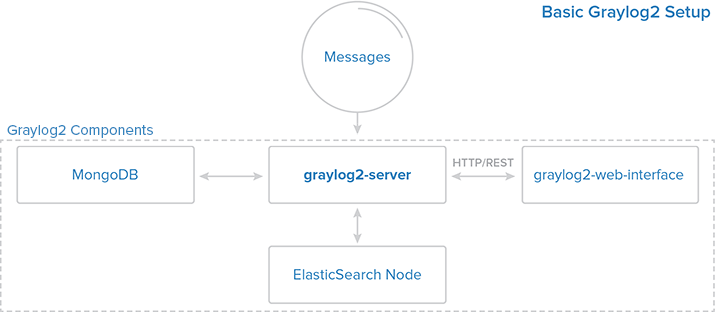
Graylog2
Graylog-server accepts and process the log messages, also spawns the RESTAPI for the requests that comes from graylog-web-interface. Download the latest version of graylog from graylog.org,
Use the following command to install graylog2 repository.
wget https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-1.2-repository-ubuntu14.04_latest.deb
dpkg -i graylog-1.2-repository-ubuntu14.04_latest.deb
Install https suppport and update the repository cache.
apt-get install apt-transport-https
apt-get update
Install Graylog server using following command.
apt-get install graylog-server
Edit the server.conf file.
nano /etc/graylog/server/server.conf
Configure the following variables in the above file.
Set a secret to secure the user passwords, use the following command to generate a secret, use at least 64 character’s.
pwgen -N 1 -s 96
OH9wXpsNZVBA8R5vJQSnkhTB1qDOjCxAh3aE3LvXddtfDlZlKYEyGS24BJAiIxI0sbSTSPovTTnhLkkrUvhSSxodTlzDi5gP
If you get a “pwgen: command not found“, use the following command to install pwgen.
apt-get install pwgen
Place the secret.
password_secret = OH9wXpsNZVBA8R5vJQSnkhTB1qDOjCxAh3aE3LvXddtfDlZlKYEyGS24BJAiIxI0sbSTSPovTTnhLkkrUvhSSxodTlzDi5gP
Next is to set a hash password for the root user (not to be confused with system user, root user of graylog is admin). You will use this password for login into the web interface, admin’s password can not be changed using web interface, must edit this variable to set.
Replace “yourpassword” with the choice of your’s.
echo -n yourpassword | sha256sum
e3c652f0ba0b4801205814f8b6bc49672c4c74e25b497770bb89b22cdeb4e951
Place the hash password.
root_password_sha2 = e3c652f0ba0b4801205814f8b6bc49672c4c74e25b497770bb89b22cdeb4e951
You can setup email address root (admin) user.
root_email = "cyber.web@gmail.com"
Set timezone of root (admin) user.
root_timezone = UTC
Graylog will try to find the Elasticsearch nodes automatically, it uses multicast mode for the same. But when it comes to larger network, it is recommended to use unicast mode which is best suited one for production setups. So add the following two entries to graylog server.conf file, replace ipaddress with live hostname or ipaddress. Multiple hosts can be added with comma separated.
elasticsearch_http_enabled = false elasticsearch_discovery_zen_ping_unicast_hosts = ipaddress:9300
Set only one master node by defining the below variable, default setting is true, you must set it as a false to make the particular node as a slave. Master node performs some periodic tasks that slave won’t perform.
is_master = true
The following variable sets the number of log messages to keep per index, it is recommended to have several smaller indices instead of larger ones.
elasticsearch_max_docs_per_index = 20000000
The following parameter defines to have total number of indices, if the this number is reached old index will be deleted.
elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices = 20
Shards setting is really depends on the number of nodes in the Elasticsearch cluster, if you have only one node, set it as 1.
elasticsearch_shards = 1
The number of replicas for your indices, if you have only one node in Elasticsearch cluster; set it as 0.
elasticsearch_replicas = 0
Restart Graylog service.
service graylog-server restart
Enable auto start of graylog server service during system startup.
update-rc.d graylog-server defaults
You can check out the server startup logs, it will be useful for you to troubleshoot graylog in case of any issue.
tailf /var/log/graylog-server/server.log
On successful start of graylog-server, you should get the following message in the log file.
2015-09-17T09:35:22.895+02:00 INFO [ServerBootstrap] Graylog server up and running.
Install Graylog web interface:
To configure graylog-web-interface, you must have at least one graylog-server node. Install Graylog web interface using “apt-get”.
apt-get install graylog-web
Edit the configuration file and set the following parameters.
nano /etc/graylog/web/web.conf
This is the list of graylog-server nodes, you can add multiple nodes, separate by commas.
graylog2-server.uris="http://127.0.0.1:12900/"
Set the application scret and can be generated using pwgen -N 1 -s 96.
application.secret="sNXyFf6B4Au3GqSlZwq7En86xp10JimdxxYiLtpptOejX6tIUpUE4DGRJOrcMj07wcK0wugPaapvzEzCYinEWj7BOtHXVl5Z"
Set Web interface timezone.
Timezone="Europe/Tallinn"
Restart the gralog-web-interface using following command,
service graylog-web restart
Enable auto start of web interface service during system startup.
update-rc.d graylog-web defaults
Netdata Monitoring
Linus Distribution: Debian Linux and its derivatives (including Ubuntu, Mint)
Install nessesary packages:
Install the packages for having a basic netdata installation (system monitoring and many applications, without mysql / mariadb, postgres, named, hardware sensors and SNMP):
curl -Ss 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firehol/netdata-demo-site/master/install-required-packages.sh' >/tmp/kickstart.sh && bash /tmp/kickstart.sh netdata
Install all the required packages for monitoring everything netdata can monitor:
curl -Ss 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firehol/netdata-demo-site/master/install-required-packages.sh' >/tmp/kickstart.sh && bash /tmp/kickstart.sh netdata-all
apt-get install zlib1g-dev uuid-dev libmnl-dev gcc make git autoconf autoconf-archive autogen automake pkg-config curl
Install Netdata
Download it - the directory 'netdata' will be created
git clone https://github.com/firehol/netdata.git --depth=1 cd netdata
Build it, install it, start it
./netdata-installer.sh
starting netdata at boot
Copy the netdata startup file to /etc/init.d
cp system/netdata-lsb /etc/init.d/netdata
Make sure it is executable
chmod +x /etc/init.d/netdata
Enable it
update-rc.d netdata defaults
Referenced : https://github.com/firehol/netdata/wiki/Installation
Nagios Monitoring
Experiences
In during installation time, we have found some problems which will impact on our your installation as well.
- The version of Ubuntu and Graylog might conflict each other as well as Graylog's packages ( e.g : java )
Summary
During the installation Graylogs in both versions of Ubuntu ( 14.04 and 16.0 ). We realized that it had many differences between these versions. Listed above our objectives what we expect to achieve after installing and using Graylog, along with its useful information and its interaction between Administrator (users) with Graylog.
its advantages:
+ Free. + Easy to interact with web interface. + Easy to install with the good support from its sources. + Help Administrator (user) to collect information in during logging and monitoring straightforwardly. + Many useful tools ( plugins ) which supports to work on.
References
http://www.itzgeek.com/how-tos/linux/ubuntu-how-tos/how-to-install-graylog2-on-ubuntu-14-04.html