BackBox OS
BackBox Linux
What is BackBox
BackBox is an open source Ubuntu based Linux distribution. Its main purpose is to provide a desktop environment for network and systems analysis, penetration and security assessment. It is a community project and full of some of the most commonly used security and analysis tools. It runs a desktop environment based on the XFCE window manager, which makes it very easy to use.
BackBox Features
- Forensic Analysis
- Information Gathering
- Vulnerability Assessment
- Exploitation
- Privilege Escalation
- Maintaining Access
- Social Engineering
- Wireless Analysis
- Documentation and Reporting
- Reverse Engineering
- VoIP Analysis
Installing and Tuning
System requirements for the latest version (4.7):
- 32-bit or 64-bit processor
- 1024 MB of system memory (RAM)
- 10 GB of disk space for installation
- Graphics card capable of 800×600 resolution
- DVD-ROM drive or USB port (3 GB)
Since this is a free and open sourced project, BackBox Linux .iso file can be downloaded from the projects homepage. The installation and tweaking of the system follows up the usual Ubuntu/Debian guide lines.

After the installation, the user can start configuring and using the services available in this operating system. This can be achieved by simply left-clicking on the blue 'B' button on the upper-left corner.
Information Gathering
Gathering information should be the first step in any security project. Without it, it would be hard to evaluate any system.
Some of the tools used in BackBox for information gathering are:
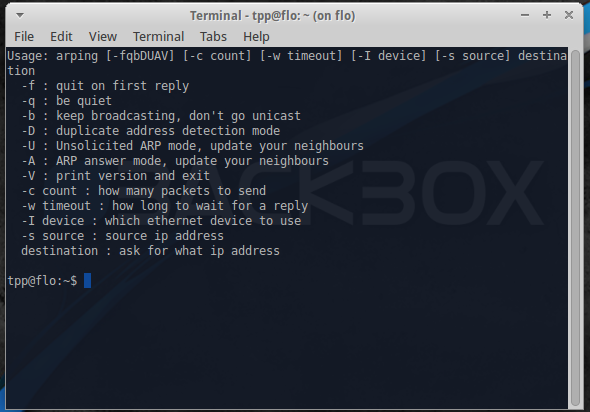
Arping
This utility sends ARP requests to the hosts on a specific subnet.
Example command:
sudo arping -I eth0 -c 3 192.168.1.1
This finds out the reachability of an IP on the local Ethernet. The '-I' identifies the intended interface, the '-c' is the count of the ARP requests taken.
Arp-scan
This is a simple but very powerful command-line tool that can be used for system discovery and fingerprinting. It assembles and sends ARP requests to specified IP addresses, displaying any responses that are received.
Example use is finding all local IP's and MAC addresses with this command:
sudo arp-scan -l
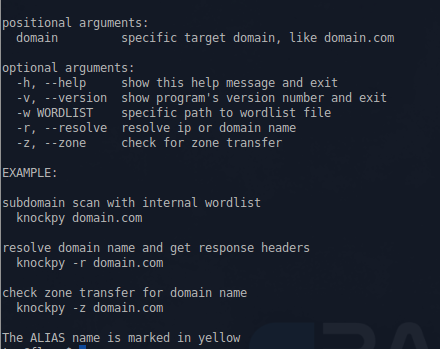
Knock
This is a Python script, written by Gianni 'guelfoweb' Amato, designed to enumerate sub-domains on a target domain through a word-list.
Example command would be this:
knockpy domain.com
This would start looking for the aforementioned site's subdomains. This is helpful if you are looking for subdomain takeover vulnerabilities.
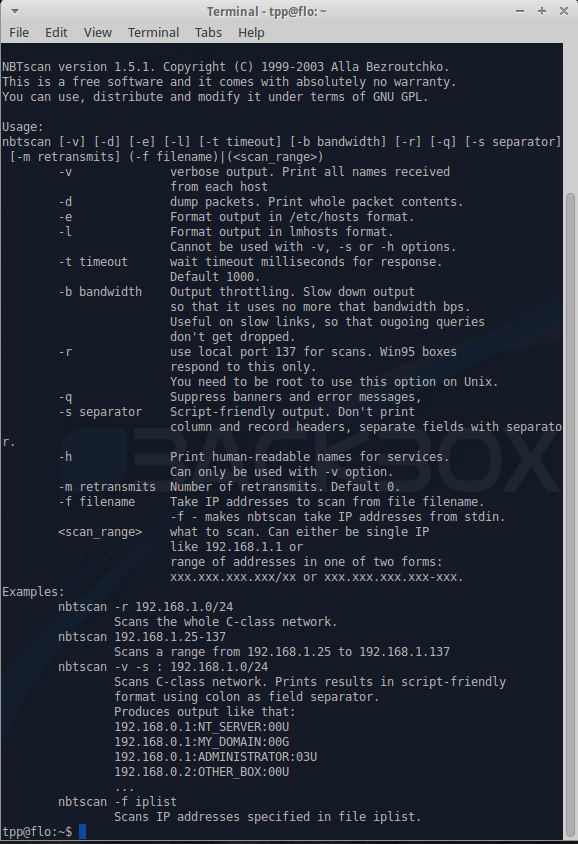
Nbtscan
This is an application to scan and get information about IP networks for NetBIOS name information.
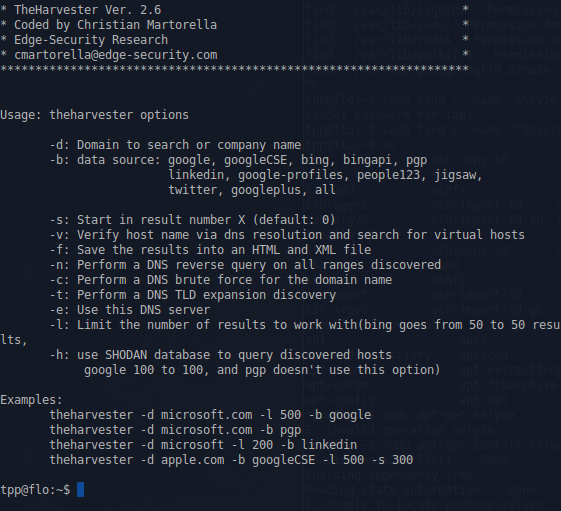
theHarvest
This is an information collector used to harvest e-mails, subdomains, hosts, and personal information about individuals.
Example command:
theharvester -d domain.com -b google
This would print all the email addresses in the site 'domain.com' that can be found by the google search engine.
Zenmap
This is the official Nmap Security Scanner GUI frontend.
Recon-ng
This is a full-featured Web Reconnaissance framework.
WhatWeb
This is an application that recognizes web technologies including content management systems (CMS), blogging platforms, statistic/analytics packages, JavaScript libraries, web servers, and embedded devices.
==== Creepy ====This is a web application security assessment report generator.
Vulnerability Assessment
Cvechecker
This is a tool that generates a report about possible vulnerabilities in your system by comparing the result with the information in its common vulnerability environment (CVE) database.
RIPS
This is a static source code analyzer for vulnerabilities in PHP web applications.
OpenVAS
This is a framework composed of several services and tools to deliver a comprehensive, powerful vulnerability scanning management solution.
Nikto
This is a web server scanner that tests web servers for dangerous files/CGIs, outdated server software, and other problems.
Skipfsh
This is an active web application security reconnaissance tool. It prepares an interactive sitemap for a targeted site by undertaking a recursive crawl and dictionary-based probes.
ZAP
This is a web application vulnerability finder (Zed Attack Proxy by OWASP)
Exploitation
Sqlmap
This is an automated tool to detect other exploiting SQL flaws.
MSF
This is a useful auditing tool that contains a lot of exploits and a development environment to modify or create them.
Armitage
This is the graphical frontend of the Metasploit Framework.
Fimap
This is a web application auditing tool for fle inclusion bugs in web apps.
Htexploit
This is a useful tool to exploit the .htaccess files
Joomscan
This is a tool that detects file inclusion, SQL injection, and command execution vulnerabilities of a targeted website that uses Joomla.
W3af
This is a GUI-based web application attack and audit framework to fnd and exploit the vulnerabilities detected.
Wpscan
This is a black box WordPress vulnerability scanner
Privilege Escalation
Dictstat
This is a password profling tool.
Maskgen
This is an analyzer for output fle produced by DictGen to generate optimal password mask collection for input to the Hashcat password cracker.
Policygen
This tool helps to generate passwords to be compliant for many policies.
Rulegen
This implements password analysis and rule generation for the Hashcat password cracker.
Hashcat
This is incredibly the fastest CPU-based password recovery tool.
Chntpw
This is a utility used for resetting or blanking local passwords in Wintel systems.
Crunch
This is a wordlist generator where you can specify a standard character set.
Fcrackzip
This is a fast password cracker partly written in assembler.
John
This (also known as John the Ripper) is a password cracking software tool.
Ophcrack
This is a Windows password cracker based on rainbow tables.
Pdfcrack
This is a tool for recovering passwords and content from PDF fles.
Truecrack
This is a brute-force password cracker for TrueCrypt (Copyright) volume fles.
Fang
This is a multiservice threaded MD5 cracker.
Medusa
This is a speedy, massively parallel, modular, login brute-force attacker, supporting many protocols.
Xhydra
This is a parallelized login cracker that can attack protocols such as TELNET, FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, HTTP-PROXY, LDAP, SMB, SMBNT, MS-SQL, MySQL, REXEC, SOCKS5, VNC, POP3, IMAP, NNTP, PCNFS, ICQ, Cisco auth, Cisco enable, and Cisco AAA by using the Telnet module.
Driftnet
This is an application that listens to network traffc and picks out images from the TCP streams it observes.
Dsniff
This is a network traffc sniffer that analyzes and parses different application protocols by extracting the relevant information.
Ettercap
This is a comprehensive suite for man-in-the-middle attacks. It has a user-friendly GUI interface and supports passive and active dissection of the amount of protocols.
Ngrep
This (also known as network grep) is a network packet analyzer.
Sslsniff
This is an SSL traffc sniffer.
Sslstrip
This is a sniffer against secure socket layer protocol.
Tcpdump
A command line packet sniffer that prints out a description of the contents of packets on a network interface that match the boolean expression.
Command to capture data from a certain interface:
sudo tcpdump -i eth0
Commant that prints out all packets arriving or departing from host PC1:
sudo tcpdump host PC1
Command that prints all IP packets between PC1 and not PC2:
sudo tcpdump host PC1 and not PC2
Wireshark
Formerly known as Etheral, it is the world's foremost network protocol analyzer.
To start capturing packets with your user, first you need to make sure that your user belongs to the usergroup named 'wireshark'. To be sure of that, use this command:
grep 'wireshark' /etc/group
If your username does not appear in the following output, it is not part of the group. To add your user to the group, use the following command:
sudo usermod -a -G wireshark yourusername
Now you can oped the Wireshark GUI, choose the network interface that is functional and start capturing and analyzing packets.
Tshark
A terminal oriented version of Wireshark. For example, to start off, you would want to know the available interfaces you can use with the command:
sudo tshark -D
An example of capturing network data with tshark:
tshark -eth0 -c 100 -w log.pcap
This will capture 100 network packets and save them into a file called log.pcap.
With the following example, we extract data from any HTTP request. The '-Y' is used to request filters, '-T' is used to specify the extract process and the '-e' is used to identify the wanted fields:
tshark -i eth0 -Y HTTP.request -T fields -e http.host -e http.user_agent
This command basically prints out the same output as Wireshark GUI:
tshark -r ~/dhcp.pcap -V frame.number == 1
Documentation and Reporting
Dradis
This is an open source information sharing framework especially designed for security assessments.
MagicTree
This is a penetration test productivity tool. This is designed to allow easy and straightforward data consolidation, querying, external command execution, and report generation.
Social Engineering
Honeyd
This is a small daemon that creates virtual hosts on a network.
Thpot
This is a tiny honeypot to set up simple and fake services.
SET
This (also known as Social-Engineer Toolkit) is designed to perform attacks against human interaction.
BeEF
This is a penetration testing tool that focuses on web browsers.
Websploit
This is used to scan and analyze remote systems in order to fnd various types of vulnerabilities.
Maintaining Access
Iodine
This is a free (ISC licensed) tunnel application to forward IPv4 traffc through DNS servers.
Ptunnel
This is an application that allows you to reliably tunnel TCP connections to a remote host using ICMP echo request and reply packets, commonly known as ping requests and replies
Weevely
This is a stealth PHP web shell that simulates a telnet-like connection
Reverse Engineering
==== Bokken ==== This is a GUI for the Pyew and Radare projects, so it offers almost all the same features that Pyew has and some features of Radare as well. It's intended to be a basic disassembler, mainly to analyze malware and vulnerabilities.
Dissy
This is a graphical frontend to the objdump disassembler.
Flasm
This is a command-line assembler/disassembler of Flash ActionScript bytecode.
Ghex
This is a simple binary GUI hex editor.
Nasm
This is a network wide assembler tool.
Ndisasm
This is a Netwide Disassembler, an 80 x 86 binary fle disassembler.
Wireless Analysis
Aircrack-ng
This is a network software suite consisting of a detector, packet sniffer, WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis tool for 802.11 wireless LANs.
Mdk3
This is a proof-of-concept tool to exploit common IEEE 802.11 protocol weaknesses.
Pyrit
This is an application GPGPU-driven WPA/WPA2-PSK key cracker.
Reaver
This is an application to perform brute-force attacks against Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS)
Wifte
This is an automated wireless auditing tool.
Wirouterkeyrec
This is a tool to recover the default WPA passphrases of supported router models.
Kismet
This is an 802.11 layer2 wireless network identifer and passive data package collector
Other Useful Features
Anonymous mode
This feature allows the use of Tor as an integrated feature, so the users are guaranteed anonymity when they surf the web.
To achieve this, push the blue button on the upper left corner, search 'tor' and then choose 'tor start' (or use the terminal command 'sudo service tor start'). After this, start the anonymous application, located at anonymous > anonymous start (or run terminal command 'anonymous start'). When this is done, you need to configure (with admin privileges) your /etc/tor/torrc file and add the following to it:
VirtualAddrNetwork 10.192.0.0/10 AutomapHostsOnResolve 1 TransPort 9040 DNSPort 53
After this, restart the tor service:
sudo service tor restart
Then start the anonymous application again. In the opened terminal window, the application will let you know that it has stopped the service network-manager, killed certain processes to prevent leaks and changed your MAC address (anonymous cannot change the MAC address in a virtual machine). Then it will ask weather the local hostname should be changed and if traffic should be transparently routed through tor. After this, you can check your settings with the command:
anonymous status
You can check weather your tor service is operable by going to check.torproject.org. You can also check weather your IP address has changed by going to whatismyipaddress website.
Sipcrack
This is a set of utilities to perform sniffng and cracking of SIP protocols.