Onions can make people cry
Intro
This wiki will cover the most important aspects of Tor: the free and open-source software that enables anyone to communicate anonymously on the internet. The article will contain a little about the deep, dark and surface web, why use Tor and what is for, the history of Tor, a closer look on how Tor actually works and the legal and illegal aspects of the web browser.
The three webs
The World Wide Web (WWW) consists of multiple parts named: deep, dark and surface web.
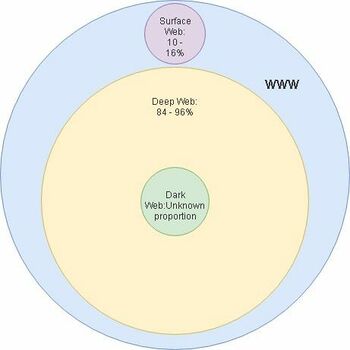
Surface web
The surface web is the easiest to explain as that is the part of the web that all of us use to browse the internet, even right now as you are reading this wiki you are browsing the surface web. The different areas of the web are defined by if they are indexed and if the user needs to authenticate himself to access the webpage. The surface web mostly consists of web pages that do not need user authentication. The web pages are indexed, meaning that a user can find the pages from using a search engine. The surface web contains about 10-16% of all of the information on the WWW. (9)
Deep web
Everything except the surface makes up the deep web part of the WWW. This means that the dark web is also a part of the deep web. Most of the deep web is inaccessible to normal search engines since the pages are not indexed or they require authentication to access. To access the deep web users need to use a special browser like Tor. Users also need to use the Hidden Wiki to get the urls for the different webpages, so the Hidden Wiki is kind of like a gateway into the deep web. The deep web contains about 84-90% of all of the information on the WWW. (9)
Dark web
And now finally, the dark web. The dark web is a part of the deep web and it’s full size is not actually known. Security experts estimate that there are about 10,000 to 100,000 active sites in the dark web at any given moment. Since the dark web is a part of the deep web it’s pages are not indexed and cannot be found by search engines. The dark web is also the part of the web where most illegal drugs, guns and human trafficking happens, but governments and the UN has also used the dark web to protect political dissidents and hunt down criminals. A great example of this is how the US government tracked down the owner of Silk Road (an underground black market primarily for drugs), Ross Ulbricht in 2013. (9)
Why use Tor
So after all of that why would you use The Onion Router (Tor)? So using Tor is similar to any other web browser, except your real IP address and any other system information is obscured when browsing the web. It also hides the user’s activity from their internet service provider.
The primary uses of Tor are:
- Bypassing censorship and surveillance
- Visiting websites anonymously
- Accessing Tor hidden services (.onion sites)
We will get into more detail about Tor and how it works later on. (9)
History
So, now that we have the basics covered let’s look at an overview of the history of The Onion Router (Tor). The idea of onion routing began in the mid 1990s and the developers of the project believed that internet users should have private access to an uncensored web. In the 1990s internet security was a really big issue and its ability to be used for tracking and surveillance was becoming clear. Therefore, 3 US Naval Research Lab (NRL) employees: Paul Sysverson, David Goldschlag and Mike Reed decided to create and deploy the first research designs and prototypes of onion routing. From its inception in the 1990s, onion routing relied on a decentralized network that used nodes that were operated by different entities with diverse interests and trust assumptions. Also the software needed to be free and open-source to maximize transparency and separation. (8)
In the early 2000s, Roger Dingledine, a MIT graduate, started working on a NRL onion routing project with Paul Syverson. Other onion routing efforts were already made, so to make this project special, they decided to call it Tor - The Onion Router. The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) recognized the benefit of Tor for digital rights and began funding the project in 2004 and in 2006 the Tor Project was founded to maintain Tor’s development. In 2007, the organization began to connect to the Tor network to address censorship, such as the need to get around government firewalls, in order for its users to access the open web. Tor was mostly popular with tech-savvy people and it was hard for less technically knowledgeable people to use, so in 2005, development of tools for the Tor proxy began and in 2008, development of the Tor browser began. (8)