SID: Difference between revisions
(New page: Eesti Infotehnoloogia Kolledź Referaat: SID Koostaja: Stanislav Tsvetajev rühm: IA37 Tallinn 2010.a Sissejuhatus Paljud oranisatsioonid ja s...) |
No edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Koostaja: Stanislav Tsvetajev | Koostaja: Stanislav Tsvetajev | ||
Rühm: IA37 | |||
Sissejuhatus | == Sissejuhatus == | ||
Paljud oranisatsioonid ja suurimad ettevõtted kasutavad kõvaketta kloonimist, et säilitada sellega oma tööaega, ei unune teatud tarkvara install, õiguste seadistamist jne. Arvuti on võimalik kasutajale püsti panna teatud minutitega, mis kuluks muidu pool päeva. | Paljud oranisatsioonid ja suurimad ettevõtted kasutavad kõvaketta kloonimist, et säilitada sellega oma tööaega, ei unune teatud tarkvara install, õiguste seadistamist jne. Arvuti on võimalik kasutajale püsti panna teatud minutitega, mis kuluks muidu pool päeva. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 9: | ||
Kui see meetod sälitad tohutolt aega on sellel meetodil spetsiifiline probleem ja see on SID ehk Security Identification. Iga kloonitud arvuti, kasutaja, grupp omavad oma SID´i. | Kui see meetod sälitad tohutolt aega on sellel meetodil spetsiifiline probleem ja see on SID ehk Security Identification. Iga kloonitud arvuti, kasutaja, grupp omavad oma SID´i. | ||
== Kloonimine ja alternatiivsed meetodid == | |||
Üks kõige populaarseimaid meetodeid on ettevõttes kloonimine. Süsteemi administraator installib valmis masinast teatud tarkvaraga nagu näiteks Ghoust ja PowerQuest. Peale imagi valmistamist on ta võimeline ümber kopperima see samune image tuhandetele arvutitele, mis säästab talle väga palju aega. | Üks kõige populaarseimaid meetodeid on ettevõttes kloonimine. Süsteemi administraator installib valmis masinast teatud tarkvaraga nagu näiteks Ghoust ja PowerQuest. Peale imagi valmistamist on ta võimeline ümber kopperima see samune image tuhandetele arvutitele, mis säästab talle väga palju aega. | ||
| Line 68: | Line 19: | ||
SID duplikatsiooni probleemid | |||
== SID duplikatsiooni probleemid == | |||
| Line 75: | Line 28: | ||
Näide dubleeritud SID´ist: | |||
== Näide dubleeritud SID´ist: == | |||
Oletame meil on ettevõttes kaks töömasinat masin1 ja masin2. Süsteemi admin kasutas tarkvara, et kloonida süsteemi teisele masinale. | Oletame meil on ettevõttes kaks töömasinat masin1 ja masin2. Süsteemi admin kasutas tarkvara, et kloonida süsteemi teisele masinale. | ||
| Line 105: | Line 60: | ||
502 – KRBTGT S-1-5-21----502 | 502 – KRBTGT S-1-5-21----502 | ||
512 - | 512 - Domeeni Admins S-1-5-21----512 | ||
513 - | 513 - Domeeni Users S-1-5-21----513 | ||
514 - | 514 - Domeeni Guest S-1-5-21----514 | ||
515 - | 515 - Domeeni Computers S-1-5-21----515 | ||
516 - | 516 - Domeeni Controllers S-1-5-21----516 | ||
517 - Cert Publishers S-1-5-21----517 | 517 - Cert Publishers S-1-5-21----517 | ||
518 - Schema Admins S-1-5-21----518 | 518 - Schema Admins S-1-5-21----518 | ||
| Line 116: | Line 71: | ||
533 - RAS and IAS Servers S-1-5-21----533 | 533 - RAS and IAS Servers S-1-5-21----533 | ||
Well Known SIDs | == Well Known SIDs == | ||
• SID: S-1-0 | • SID: S-1-0 | ||
| Line 310: | Line 266: | ||
• SID: S-1-9 | • SID: S-1-9 | ||
Name: Resource Manager Authority An identifier | Name: Resource Manager Authority An identifier | ||
== Meetodid: == | |||
On olemas palju meetodeid, kuidas SID unikaalset numbrit muuta. Miks on vaja seda teha, see oli mainitud ees pool. Muuta on võimalik käsitsi või kasutades tarvara. Takvarad millega oleks võimalik see teoks viia on Sysprep või NEWSID. Pole kasutanud Sysprepi, kui nii palju kui olen materjale lugenud on NEWSID tükkmaad kiirem ümberkirjutamis protsess. | |||
'''NEWSID''' | |||
Kui käivitate NEWSIDi on Teie ees väike tervitad tekst: | |||
[[Image:newSid1.jpg]] | |||
Vajutage Next | |||
[[Image:newSid2.jpg]] | |||
Teie ees on väike aken erinevate võimalustega, soovitan valida Random, kuna siis ta genereerib unikaalse SID, mitte copy või spetsifiline SID, mida trükite ise sisse: | |||
[[Image:newSid3.jpg]] | |||
Selles valitud lahenduses on võimalik Teil muuta korraga nii arvuti nimi, kui ka SID. Soovitan valida mõlemaid, juhul kui Teie arvuti on ühendatud otse võrku ja selle tõttu vältida konflikte. | |||
Kui olen valinud arvutile uue nime siis vajutage Next | |||
[[Image:newSid4.jpg]] | |||
Viimane aken kus näitab Teile mis valikud Te olete osutanud, vajutades Next. Genereerib Teie arvutile programm mõningate minutitega vajalikud seadistused, kõik sõltub registri suurusest. | |||
== Kasutatud materjal: == | |||
1. [http://telnetport25.wordpress.com/page/31/ http://telnetport25.wordpress.com/page/31/] | |||
2. [http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897418.aspx http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897418.aspx] | |||
3. [http://servermigrator.blogspot.com/2006/02/why-understanding-sids-is-important.html http://servermigrator.blogspot.com/2006/02/why-understanding-sids-is-important.html] | |||
= Autor = | |||
Stanislav Tsvetajev IA37 | |||
[[Category: Windows Server administreerimine]] | |||
Latest revision as of 10:50, 29 March 2010
Koostaja: Stanislav Tsvetajev Rühm: IA37
Sissejuhatus
Paljud oranisatsioonid ja suurimad ettevõtted kasutavad kõvaketta kloonimist, et säilitada sellega oma tööaega, ei unune teatud tarkvara install, õiguste seadistamist jne. Arvuti on võimalik kasutajale püsti panna teatud minutitega, mis kuluks muidu pool päeva.
Kui see meetod sälitad tohutolt aega on sellel meetodil spetsiifiline probleem ja see on SID ehk Security Identification. Iga kloonitud arvuti, kasutaja, grupp omavad oma SID´i.
Kloonimine ja alternatiivsed meetodid
Üks kõige populaarseimaid meetodeid on ettevõttes kloonimine. Süsteemi administraator installib valmis masinast teatud tarkvaraga nagu näiteks Ghoust ja PowerQuest. Peale imagi valmistamist on ta võimeline ümber kopperima see samune image tuhandetele arvutitele, mis säästab talle väga palju aega.
Järgmine populaarne meetod on kasutada Microsoft sysdiff utility. See tuul nõuab et süsteemi administraator esitleks täis installatsiooni (tavaliselt unattended skripti installatsioon) igale arvutile ja siis sysdiff automatiseerib tarkvara image add-on aplikatsiooni.
Seepärast on selline installatsiooni meetod kõlbmatu ja seepärast on ketta sektori kloonimine palju efektiivsem kui filide kopimine. Süsteemi administraator ei pea õppima kuidas unattended installatsiooni teha või sysdiff ning valmistada ja otsida skriptides vigu.
SID duplikatsiooni probleemid
Kui igale arvutile tehakse puhas install saab ta unikaalse nime ja SID´i. Kuid kui süsteem on kloonitud siis omab ta dubleeritud SID. Kui vahetada arvuti nime või panna teda teise workgroupi ei ole sellest abi.
Näide dubleeritud SID´ist:
Oletame meil on ettevõttes kaks töömasinat masin1 ja masin2. Süsteemi admin kasutas tarkvara, et kloonida süsteemi teisele masinale.
Aleksi masin omab lokaal kontot ja masin1 omab S-1-5-34-148593445-285934854-2859284934-1010
Kevin masin omab lokaal kontot ja masin2 omab S-1-5-34-148593445-285934854-2859284934-1010
Aleks kasutaja salvestab oma infot NTFS kettale ja tekitab jagatud kausta nimega privaat see mida tema saab ainult näha (siseneda). Kui Kevin vaataleb võrgus jagatud olevaid kaustasin on ta võimeline sellesse sisse saama kuna ta omab identset SID´i mida Alekski. Oletame, et võrgus on sada masinat installitud sama SID´iga siis ei oma te mingit turvalisust oma võrgus. Isegi kõik faildi mis on removeable meedia salvestatud on sammuti haavatud.
SID´i sügavus
Nagu näete näidest tavapärane SID näeb välja nii S-1-5-12-7723811915-3361004348-033306820-1006. SID numbriline tähendus on järgmine:
S – String on SID 1 – redigeerimise aste. 5 – autoriteedi identifitseerimine 12–7723811915-3361004348-033306820 Domeeni või local arvuti indentifitseerimine 1006 – RID
Iga grupp või kasutaja, kes ei olnud tekitatud defaultina omab RID 1000 või suurem. RID on Registeri ID. See on SID viimane portsion. Kui RID on väljalastud, peale seda ei kasutata teda enam välja arvatud kui konto on kustutatud.
Kuigi on alati aksepteeritav MS Windowsis. Teatud RID (alla 1000) on defineeritud:
500 - Administrator S-1-5-21----500 501 - Guest S-1-5-21----501 502 – KRBTGT S-1-5-21----502
512 - Domeeni Admins S-1-5-21----512 513 - Domeeni Users S-1-5-21----513 514 - Domeeni Guest S-1-5-21----514 515 - Domeeni Computers S-1-5-21----515 516 - Domeeni Controllers S-1-5-21----516 517 - Cert Publishers S-1-5-21----517 518 - Schema Admins S-1-5-21----518 519 - Enterprise Admins S-1-5-21----519 520 - Group Policy Creator Owners S-1-5-21----520 533 - RAS and IAS Servers S-1-5-21----533
Well Known SIDs
• SID: S-1-0 Name: Null Authority Description: An identifier authority.
• SID: S-1-0-0 Name: Nobody Description: No security principal.
• SID: S-1-1 Name: World Authority Description: An identifier authority.
• SID: S-1-1-0 Name: Everyone Description: A group that includes all users, even anonymous users and guests. Membership is controlled by the operating system. Note By default, the Everyone group no longer includes anonymous users on a computer that is running Windows XP Service Pack 2 (SP2).
• SID: S-1-2 Name: Local Authority Description: An identifier authority.
• SID: S-1-3 Name: Creator Authority Description: An identifier authority.
• SID: S-1-3-0 Name: Creator Owner Description: A placeholder in an inheritable access control entry (ACE). When the ACE is inherited, the system replaces this SID with the SID for the object's creator.
• SID: S-1-3-1 Name: Creator Group Description: A placeholder in an inheritable ACE. When the ACE is inherited, the system replaces this SID with the SID for the primary group of the object's creator. The primary group is used only by the POSIX subsystem.
• SID: S-1-3-2 Name: Creator Owner Server Description: This SID is not used in Windows 2000.
• SID: S-1-3-3 Name: Creator Group Server Description: This SID is not used in Windows 2000.
• SID: S-1-4 Name: Non-unique Authority Description: An identifier authority.
• SID: S-1-5 Name: NT Authority Description: An identifier authority.
• SID: S-1-5-1 Name: Dialup Description: A group that includes all users who have logged on through a dial-up connection. Membership is controlled by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-2 Name: Network Description: A group that includes all users that have logged on through a network connection. Membership is controlled by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-3 Name: Batch Description: A group that includes all users that have logged on through a batch queue facility. Membership is controlled by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-4 Name: Interactive Description: A group that includes all users that have logged on interactively. Membership is controlled by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-5-X-Y Name: Logon Session Description: A logon session. The X and Y values for these SIDs are different for each session.
• SID: S-1-5-6 Name: Service Description: A group that includes all security principals that have logged on as a service. Membership is controlled by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-7 Name: Anonymous Description: A group that includes all users that have logged on anonymously. Membership is controlled by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-8 Name: Proxy Description: This SID is not used in Windows 2000.
• SID: S-1-5-9 Name: Enterprise Domain Controllers Description: A group that includes all domain controllers in a forest that uses an Active Directory directory service. Membership is controlled by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-10 Name: Principal Self Description: A placeholder in an inheritable ACE on an account object or group object in Active Directory. When the ACE is inherited, the system replaces this SID with the SID for the security principal who holds the account.
• SID: S-1-5-11 Name: Authenticated Users Description: A group that includes all users whose identities were authenticated when they logged on. Membership is controlled by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-12 Name: Restricted Code Description: This SID is reserved for future use.
• SID: S-1-5-13 Name: Terminal Server Users Description: A group that includes all users that have logged on to a Terminal Services server. Membership is controlled by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-18 Name: Local System Description: A service account that is used by the operating system.
• SID: S-1-5-19 Name: NT Authority Description: Local Service
• SID: S-1-5-20 Name: NT Authority Description: Network Service
• SID: S-1-5-32-544 Name: Administrators Description: A built-in group. After the initial installation of the operating system, the only member of the group is the Administrator account. When a computer joins a domain, the Domain Admins group is added to the Administrators group. When a server becomes a domain controller, the Enterprise Admins group also is added to the Administrators group.
• SID: S-1-5-32-545 Name: Users Description: A built-in group. After the initial installation of the operating system, the only member is the Authenticated Users group. When a computer joins a domain, the Domain Users group is added to the Users group on the computer.
• SID: S-1-5-32-546 Name: Guests Description: A built-in group. By default, the only member is the Guest account. The Guests group allows occasional or one-time users to log on with limited privileges to a computer's built-in Guest account.
• SID: S-1-5-32-547 Name: Power Users Description: A built-in group. By default, the group has no members. Power users can create local users and groups; modify and delete accounts that they have created; and remove users from the Power Users, Users, and Guests groups. Power users also can install programs; create, manage, and delete local printers; and create and delete file shares.
• SID: S-1-5-32-548 Name: Account Operators Description: A built-in group that exists only on domain controllers. By default, the group has no members. By default, Account Operators have permission to create, modify, and delete accounts for users, groups, and computers in all containers and organizational units of Active Directory except the Builtin container and the Domain Controllers OU. Account Operators do not have permission to modify the Administrators and Domain Admins groups, nor do they have permission to modify the accounts for members of those groups.
• SID: S-1-5-32-549 Name: Server Operators Description: A built-in group that exists only on domain controllers. By default, the group has no members. Server Operators can log on to a server interactively; create and delete network shares; start and stop services; back up and restore files; format the hard disk of the computer; and shut down the computer.
• SID: S-1-5-32-550 Name: Print Operators Description: A built-in group that exists only on domain controllers. By default, the only member is the Domain Users group. Print Operators can manage printers and document queues . • SID: S-1-5-32-551 Name: Backup Operators Description: A built-in group. By default, the group has no members. Backup Operators can back up and restore all files on a computer, regardless of the permissions that protect those files. Backup Operators also can log on to the computer and shut it down.
• SID: S-1-5-32-552 Name: Replicators Description: A built-in group that is used by the File Replication service on domain controllers. By default, the group has no members. Do not add users to this group. The following groups will show as SIDs until a Windows Server 2003 domain controller is made the primary domain controller (PDC) operations master role holder. (The "operations master" is also known as flexible single master operations or FSMO.)
• SID: S-1-5-32-554 Name: BUILTIN\Pre-Windows 2000 Compatible Access Description: An alias added by Windows 2000. A backward compatibility group which allows read access on all users and groups in the domain.
• SID: S-1-5-32-555 Name: BUILTIN\Remote Desktop Users Description: An alias. Members in this group are granted the right to logon remotely.
• SID: S-1-5-32-556 Name: BUILTIN\Network Configuration Operators Description: An alias. Members in this group can have some administrative privileges to manage configuration of networking features.
• SID: S-1-5-32-557 Name: BUILTIN\Incoming Forest Trust Builders Description: An alias. Members of this group can create incoming, one-way trusts to this forest.
• SID: S-1-5-32-558 Name: BUILTIN\Performance Monitor Users Description: An alias. Members of this group have remote access to monitor this computer.
• SID: S-1-5-32-559 Name: BUILTIN\Performance Log Users Description: An alias. Members of this group have remote access to schedule logging of performance counters on this computer.
• SID: S-1-5-32-560 Name: BUILTIN\Windows Authorization Access Group Description: An alias. Members of this group have access to the computed tokenGroupsGlobalAndUniversal attribute on User objects.
• SID: S-1-5-32-561 Name: BUILTIN\Terminal Server License Servers Description: An alias. A group for Terminal Server License Servers.
• SID: S-1-6 Name: Site Server Authority An identifier authority.
• SID: S-1-7 Name: Internet Site Authority An identifier authority.
• SID: S-1-8 Name: Exchange Authority An identifier authority.
• SID: S-1-9 Name: Resource Manager Authority An identifier
Meetodid:
On olemas palju meetodeid, kuidas SID unikaalset numbrit muuta. Miks on vaja seda teha, see oli mainitud ees pool. Muuta on võimalik käsitsi või kasutades tarvara. Takvarad millega oleks võimalik see teoks viia on Sysprep või NEWSID. Pole kasutanud Sysprepi, kui nii palju kui olen materjale lugenud on NEWSID tükkmaad kiirem ümberkirjutamis protsess.
NEWSID
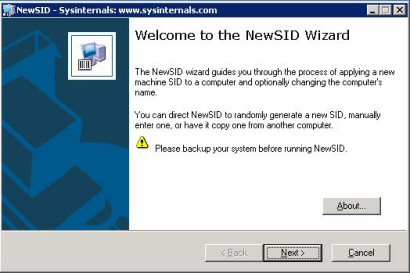
Kui käivitate NEWSIDi on Teie ees väike tervitad tekst:
Vajutage Next
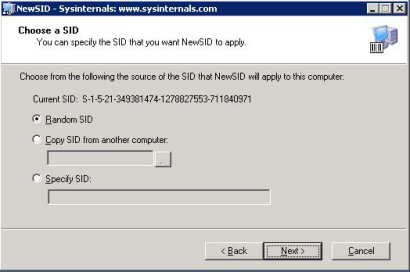
Teie ees on väike aken erinevate võimalustega, soovitan valida Random, kuna siis ta genereerib unikaalse SID, mitte copy või spetsifiline SID, mida trükite ise sisse:
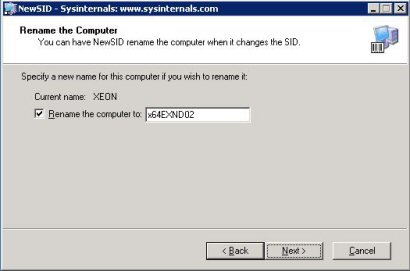
Selles valitud lahenduses on võimalik Teil muuta korraga nii arvuti nimi, kui ka SID. Soovitan valida mõlemaid, juhul kui Teie arvuti on ühendatud otse võrku ja selle tõttu vältida konflikte.
Kui olen valinud arvutile uue nime siis vajutage Next
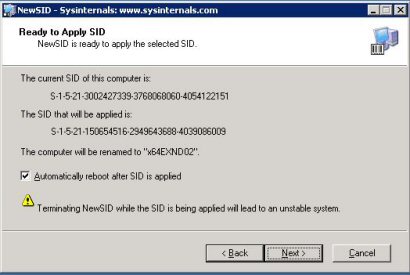
Viimane aken kus näitab Teile mis valikud Te olete osutanud, vajutades Next. Genereerib Teie arvutile programm mõningate minutitega vajalikud seadistused, kõik sõltub registri suurusest.
Kasutatud materjal:
1. http://telnetport25.wordpress.com/page/31/
2. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897418.aspx
3. http://servermigrator.blogspot.com/2006/02/why-understanding-sids-is-important.html
Autor
Stanislav Tsvetajev IA37