At: Difference between revisions
From ICO wiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
== Kasutamine ja näited == | == Kasutamine ja näited == | ||
[http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2010/06/at-atq-atrm-batch-command-examples/] | [http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2010/06/at-atq-atrm-batch-command-examples/] | ||
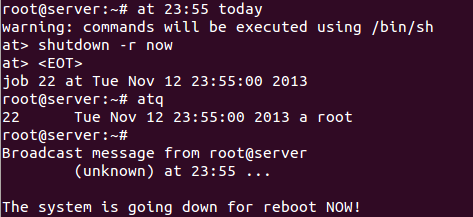
=== Töö käivitamine kindlaksmääratud kuupäeval ja ajal === | === Töö käivitamine kindlaksmääratud kuupäeval ja ajal === | ||
Revision as of 23:17, 16 December 2013
work in progress
Sissejuhatus
| at | At, koondab sisestatud käsud ühte at-job-i, mis käivitatakse hiljem. At-job pärib oma keskkonna, st. käsu käivitatakse hetkel on töökataloog ja süsteemimuutujatd samasugused nagu oli sisestamisel At, erineb cron-ist. At on korraliseks kasutamiseks, cron on selleks kui mingit käsku vaja käivitada samal ajal perioodiliselt korduvalt. |
| atq | tavakasutaja korral loendab kasutaja ootel olevad tööd superuseri korral loendab kõikide kasutajate ootel olevad tööd |
| atrm | kustutab töid, mille töönumber on täpsustatud |
| batch | käivitab käsu kui süsteemi load (koormatus) seda lubab, kui koormus langeb alla 0.8, või väärtuse mis täpsustatud atrun käsuga |
Kasutamine ja näited
Töö käivitamine kindlaksmääratud kuupäeval ja ajal
at <kellaeg> <päev>
Töö käivitamine kasutades suhtelist aega (N: nüüd + 10 minutit)
Käivitamiseks määratud tööde nimekirja kuvamine käsuga atq
Käivitamiseks määratud tööde eemaldamine/kustutamine käsuga atrm
Käivitamine, kui koormus on madalam kui < 1.5 käsuga batch
Tööde käivitamine failist kasutades -f võtit
At käsu kasutamise lubamine/piiramine teatud kasutajatele
At käsu käivitamine nohup reziimis
Täiendavad aja formaadid At käsule
Failid
/var/spool/cron/atjobs
/var/spool/cron/atspool
/proc/loadavg
/var/run/utmp
/etc/at.allow
/etc/at.deny
Võtmed (kas on mõtet sisse jätta/targem MAN lugeda ?)
-V kuvab versiooni
-q queue
uses the specified queue. A queue designation consists of a
single letter; valid queue designations range from a to z and A
to Z. The a queue is the default for at and the b queue for
batch. Queues with higher letters run with increased niceness.
The special queue "=" is reserved for jobs which are currently
running.
If a job is submitted to a queue designated with an uppercase letter,
the job is treated as if it were submitted to batch at the time of the
job. Once the time is reached, the batch processing rules with respect
to load average apply. If atq is given a specific queue, it will only
show jobs pending in that queue.
-m Send mail to the user when the job has completed even if there
was no output.
-M Never send mail to the user.
-f file Reads the job from file rather than standard input.
-t time run the job at time, given in the format [[CC]YY]MMDDhhmm[.ss]
-l Is an alias for atq.
-r Is an alias for atrm.
-d Is an alias for atrm.
-b is an alias for batch.
-v Kuvab, millal töö käivitatakse, enne töö sisselugemist.
-c cats the jobs listed on the command line to standard output.
Vead
The correct operation of batch for Linux depends on the presence of a
proc- type directory mounted on /proc.
If the file /var/run/utmp is not available or corrupted, or if the user
is not logged on at the time at is invoked, the mail is sent to the
userid found in the environment variable LOGNAME. If that is undefined
or empty, the current userid is assumed.
At and batch as presently implemented are not suitable when users are
competing for resources. If this is the case for your site, you might
want to consider another batch system, such as nqs.
Kasutatud kirjandus
http://lowfatlinux.com/linux-task-scheduler-at.html
http://linux.about.com/library/cmd/blcmdl1_atq.htm
http://www.brunolinux.com/02-The_Terminal/The_at_Command.html
http://www.computerhope.com/unix/uat.htm
http://www.computerhope.com/unix/ucrontab.htm
http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2010/06/at-atq-atrm-batch-command-examples/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/At_%28Unix%29
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gE9oWoKIK6o
Autor
Paul Are AK31, 2013